44+ Why Is It Called The Ring Of Fire? Ideas. The ring of fire is the geographical area around the edges of the pacific ocean. What is the cause of the ring of fire? The ring of fire sees more natural disasters than anywhere else on earth, but what makes it particularly dangerous is that few countries are prepared. Much of the volcanic activity occurs along subduction zones, which are convergent plate boundaries the trenches form because as one plate subducts under another, it is bent downward. When the plates collide, they create areas of volatility.
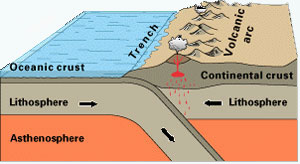
That is, the plate that is underneath is.
Why so many volcanoes in the ring of fire? The 'ring of fire' is a very 'high volcanic and seismic' geographic area which is situated around the pacific ocean's edges. The ring of fire is a ring of volcanoes around the pacific ocean that result from subduction of oceanic plates beneath lighter continental plates. Part of a larger subduction zone, it contains the deepest point of any ocean on earth. The list that will follow shortly will try to answer all these four questions in the most concise fashion possible. The area encircling the pacific ocean is called the ring of fire, because its edges mark a circle of high volcanic and seismic activity (earthquakes). The pacific ring of fire is an arc around the pacific ocean where many volcanoes and earthquakes are formed. The world's most active volcanoes lie along what's called the ring of fire. The pacific ring of fire (or just the ring of fire) is an area where large numbers of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the in a 40,000 km (25,000 mi) horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements.